The construction industry is evolving to meet these needs by using eco-friendly materials in residential projects. In Canada, where environmental stewardship is a growing priority, builders and homeowners are seeking sustainable materials that reduce environmental impact, improve energy efficiency, and enhance the longevity of homes. This paper explores the various types of sustainable materials used in Canadian residential construction and how they contribute to a greener, more energy-efficient, and durable living environment.
The Importance of Sustainable Building Materials
Sustainable building materials play a critical role in reducing the environmental footprint of residential construction. These materials are designed to:
- Reduce Resource Depletion: Sustainable materials are often made from renewable resources or recycled content, decreasing the demand for virgin materials and minimizing waste.
- Lower Energy Consumption: Many sustainable materials contribute to energy efficiency by providing better insulation, reducing heating and cooling needs.
- Minimize Environmental Impact: Eco-friendly materials typically produce fewer emissions during manufacturing and transportation, contributing to a cleaner environment.
- Improve Indoor Air Quality: Non-toxic, low-emission materials reduce the presence of harmful chemicals in the home, promoting healthier living spaces.
Key Types of Sustainable Materials for Canadian Homes
1. Reclaimed and Recycled Materials
Using reclaimed or recycled materials helps reduce waste and lessen the demand for new resources. These materials often come from old buildings, factories, or industrial sites, and they can be repurposed for new construction projects.

a) Reclaimed Wood
Reclaimed wood, salvaged from older structures such as barns or warehouses, is widely used in Canadian homes for flooring, cabinetry, and furniture. It brings a unique aesthetic appeal while reducing the need for new lumber production.
- Benefits: Reclaimed wood reduces deforestation, has lower embodied energy compared to new wood, and often features attractive weathered textures.
- Usage: Flooring, wall cladding, cabinetry, and structural elements.

b) Recycled Steel
Recycled steel is commonly used in the framing of homes and in roofing materials. Steel can be recycled repeatedly without losing its strength, making it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional wood framing.
- Benefits: Steel is durable, requires minimal maintenance, and is often made from recycled content.
- Usage: Structural framing, roofing, and reinforcement bars.
c) Recycled Glass
Recycled glass is used in various applications, from countertops and tiles to insulation materials. Glass is a highly recyclable material, making it ideal for use in homes aiming for sustainability.
- Benefits: Reduces landfill waste and has a modern, aesthetic appeal.
- Usage: Countertops, tiles, and decorative features.
2. Bamboo
Bamboo is a fast-growing renewable resource that is increasingly being used in Canadian home construction. It is a highly sustainable alternative to traditional hardwood due to its rapid growth rate and minimal need for pesticides or fertilizers.
- Benefits: Bamboo regenerates quickly, absorbs carbon dioxide, and is highly durable.
- Usage: Flooring, cabinetry, furniture, and decorative elements.
3. Hempcrete
Hempcrete is an innovative sustainable building material made from hemp fibers mixed with a lime-based binder. It is a lightweight, carbon-negative material that provides excellent insulation and breathability.
- Benefits: Hempcrete absorbs carbon during its growth phase, making it a carbon-negative material. It is also fire-resistant, non-toxic, and provides excellent insulation.
- Usage: Wall insulation, wall construction, and flooring insulation.
4. Straw Bale
Straw bale construction is gaining popularity in Canada as a sustainable option for building insulated walls. Straw is a renewable, natural material that provides high levels of insulation and is both affordable and abundant.
- Benefits: Straw bales offer excellent thermal insulation, reducing heating and cooling costs, and are made from a renewable resource.
- Usage: Wall construction, insulation, and infill for timber frames.
5. Rammed Earth
Rammed earth construction involves compacting layers of earth, sand, and gravel to create durable, thermally efficient walls. It is an ancient building technique that has gained renewed interest in sustainable construction.
- Benefits: Rammed earth is highly durable, fire-resistant, and provides excellent thermal mass, helping to regulate indoor temperatures.
- Usage: Wall construction and thermal mass walls.
6. Low-VOC Paints and Finishes
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are chemicals commonly found in paints, stains, and finishes, and they can emit harmful fumes into the indoor environment. Low-VOC and no-VOC paints and finishes offer a healthier alternative for homeowners.
- Benefits: Reduces indoor air pollution and improves indoor air quality, contributing to a healthier living environment.
- Usage: Interior and exterior paints, wood finishes, and stains.
7. Insulated Concrete Forms (ICFs)
Insulated Concrete Forms (ICFs) are a sustainable building method that combines concrete with insulation to create energy-efficient and durable walls. ICFs provide excellent thermal performance and help reduce energy consumption.
- Benefits: ICFs are energy-efficient, durable, and provide superior soundproofing. They also reduce the overall environmental impact of construction by combining structure and insulation in one system.
- Usage: Wall construction for homes, particularly in colder climates.
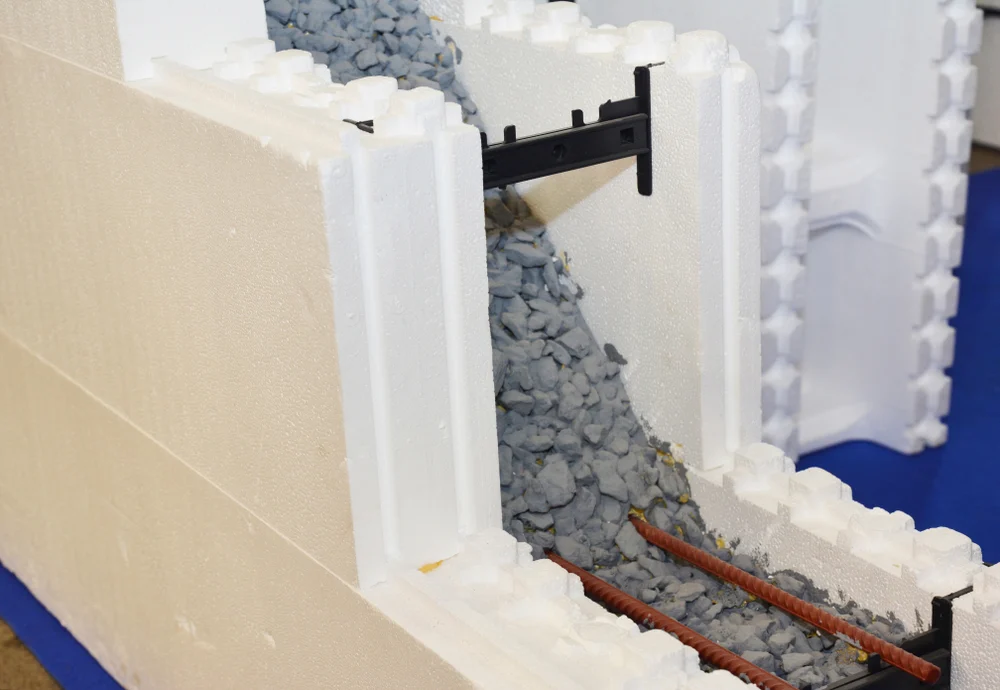

8. Cork
Cork is a renewable, natural material harvested from the bark of cork oak trees. It is a versatile and sustainable option for flooring, insulation, and wall coverings.
- Benefits: Cork is naturally insulating, sound-absorbing, and resistant to mold and mildew. It is also harvested without harming the tree, making it a highly renewable resource.
- Usage: Flooring, wall coverings, and insulation.
Energy-Efficient and Sustainable Building Systems
Beyond individual materials, incorporating sustainable building systems enhances the overall environmental performance of a home. These systems reduce energy consumption, lower utility costs, and contribute to a more sustainable living environment.
1. Solar Panels
Solar panels are becoming increasingly common in Canadian homes as the technology becomes more affordable and efficient. They provide a renewable source of energy and can significantly reduce a home’s reliance on the grid.
- Benefits: Solar panels lower energy bills, reduce carbon emissions, and increase a home’s value.
- Usage: Rooftop installations for electricity generation and water heating.
2. Green Roofs
Green roofs are vegetative layers installed on top of buildings that provide insulation and reduce the heat island effect in urban areas. They are particularly effective in urban settings where space for greenery is limited.
- Benefits: Green roofs improve air quality, provide natural insulation, and help manage stormwater runoff.
- Usage: Rooftop insulation and outdoor living spaces.
3. Rainwater Harvesting Systems
Rainwater harvesting systems collect and store rainwater for use in irrigation, flushing toilets, and even as potable water when properly treated. These systems reduce the strain on municipal water supplies and help conserve water.
- Benefits: Reduces water usage, lowers utility bills, and provides a renewable water source.
- Usage: Irrigation, toilet flushing, and domestic water use.
4. Energy-Efficient Windows
Energy-efficient windows, such as those with low-emissivity (Low-E) coatings, help reduce heat transfer, making homes more comfortable while lowering energy costs. These windows are crucial in Canada’s colder climates where heat retention is essential.
- Benefits: Reduces energy consumption, improves comfort, and lowers heating and cooling costs.
- Usage: Throughout the home, especially in areas with significant sun exposure or heat loss.
The Role of Building Codes in Sustainable Materials
In Canada, building codes and regulations are evolving to include provisions for sustainable materials and energy-efficient construction practices. The National Building Code (NBC) and the National Energy Code for Buildings (NECB) provide guidelines for energy efficiency, water conservation, and environmentally responsible building practices.
Provinces like British Columbia and Ontario have introduced additional building codes and voluntary programs, such as the BC Energy Step Code, which encourages the use of energy-efficient materials and building methods.
Conclusion
Sustainable materials are becoming increasingly important in Canadian residential construction as the demand for eco-friendly, energy-efficient homes continues to grow. From reclaimed wood and recycled steel to innovative materials like hempcrete and rammed earth, sustainable materials help reduce the environmental impact of construction while improving the energy efficiency and durability of homes. By using these materials, builders and homeowners can contribute to a greener future while creating comfortable, healthy living environments. With evolving building codes and technologies, the use of sustainable materials in Canadian homes is set to become even more widespread in the coming years.

